H Æ N E P L D N
H Æ N E P
[ Hay - nep ] noun.
_______________
[Old English] hænep. related to
[Old Norse] hampr.
[Old Dutch] hennep.
[Old High German] hanaf.
LONG FIBRE PROCESSING
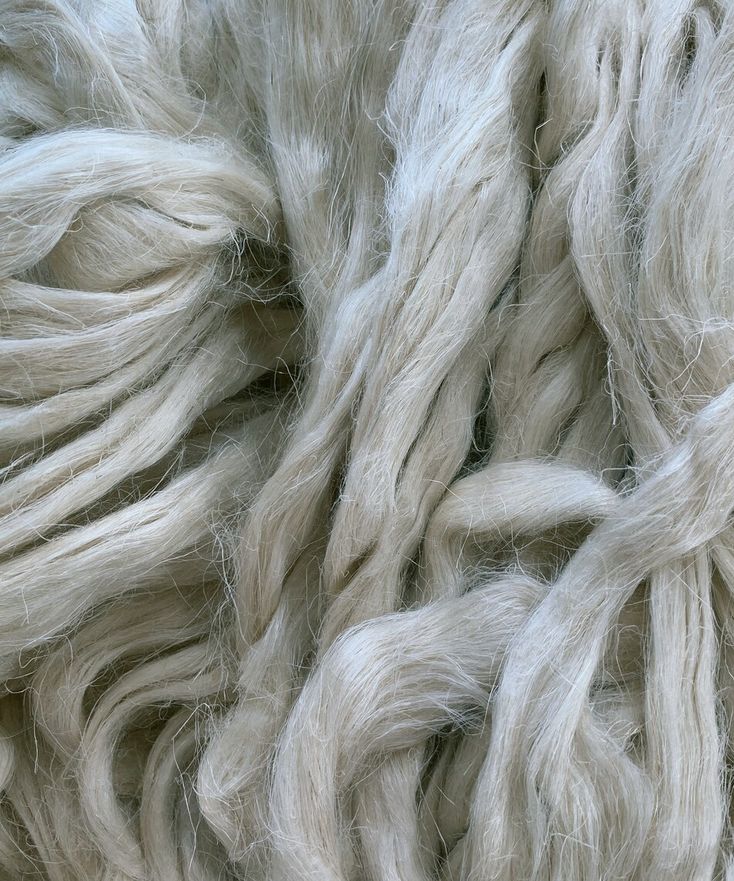
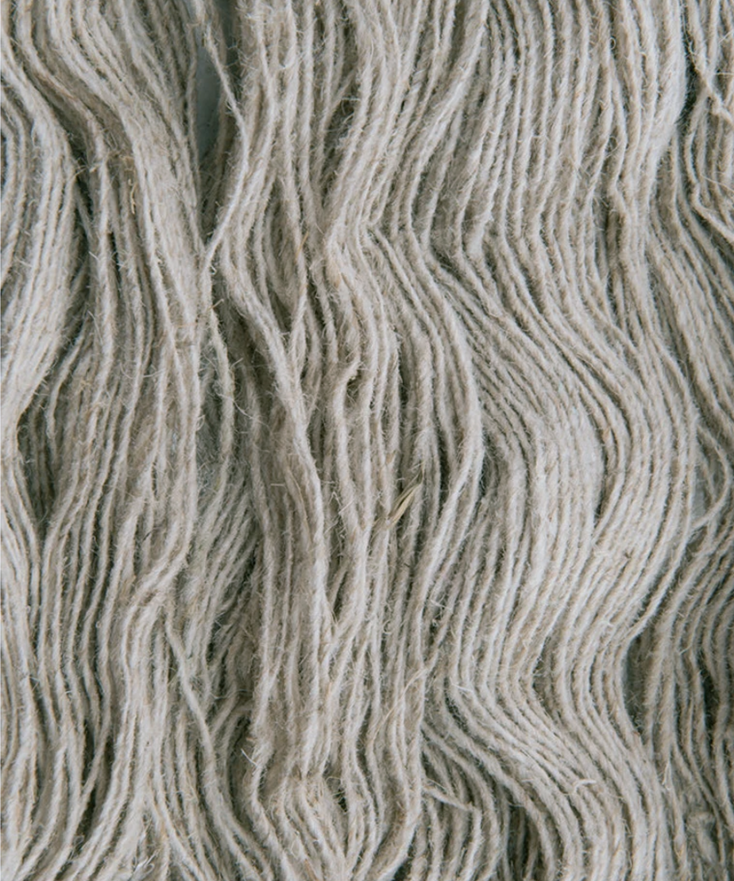
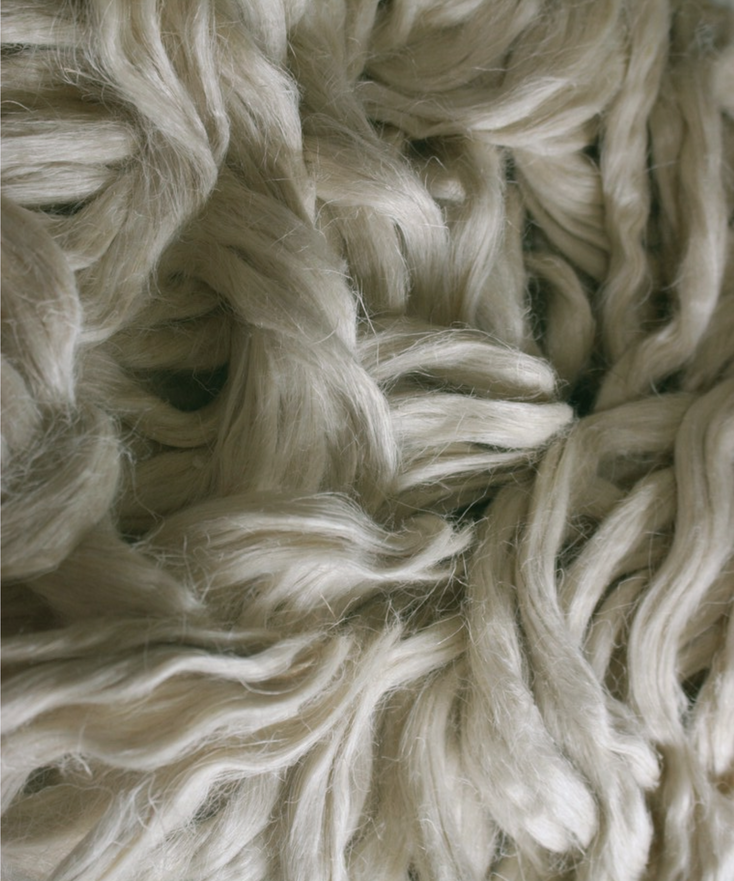
Spinning hɛmp fibre involves retting, decortication, softening, combing then spinning using wet or dry methods. Hɛmp fibre can be spun using any one of these three processes; Long fiber, Tow processing or Cottonization.
RETTING H Æ N E P FIBRE
H Æ N E P is harvested up to the mid flowering stage, which is then cut four to five feet from ground level, ensuring that both the seeds and the fibres are harvested. The plants are then left in the field to 'ret' for about 10 to 20 days. Retting is done either by water or dew.
Water retting is a process where the stems are placed in water, more specifically, in ponds, tanks or streams for approximately 10 days. While dew retting involves laying the H Æ N E P in parallel rows to absorb the morning dew. During this time, the stems are turned at least twice to allow them to ‘ret’ or rot evenly.
In either method of retting, pectin within the H Æ N E P that binds the fibres to the stem’s core is being released, which causes the fibres to separate. The process is complete once the H Æ N E P stalks have become white, and divide easily into fibres, separated from the core, and the stalks are dry.